

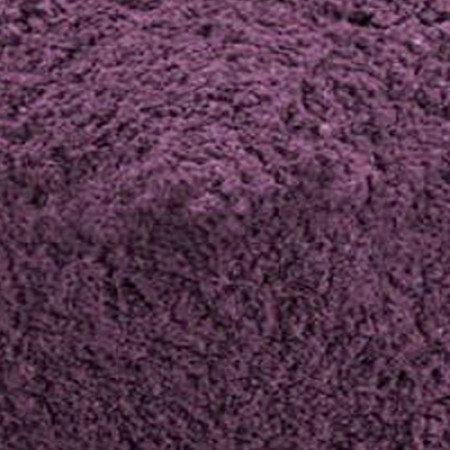
Kindah Tropical’s 100% pure Bilberry Powder
$5.60 – $86.40
Renowned for its benefits to eye health, bilberry powder is packed with anthocyanins, which improve vision and circulation. It also supports cardiovascular and cognitive health. Its tangy flavor enhances teas, smoothies, and jams.
ifferences Between Blueberries and Bilberries: Medicinal and Historical Uses
Blueberries and bilberries are closely related fruits from the Vaccinium genus, but they differ in appearance, nutrient composition, and traditional applications in medicine. Below is a comparison of their medicinal and historical uses:
1. Blueberries (Vaccinium corymbosum, Vaccinium angustifolium)
Medicinal Uses
- Antioxidant Powerhouse: Blueberries are rich in anthocyanins, which help combat oxidative stress and reduce inflammation.
- Heart Health: Regular consumption supports cardiovascular health by improving cholesterol levels and blood pressure.
- Cognitive Function: Blueberries have been linked to improved memory and delayed cognitive aging due to their neuroprotective properties.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: They help stabilize blood sugar levels, beneficial for diabetes management.
- Digestive Health: Contain dietary fiber that supports gut health and regularity.
Historical Uses
- Native Americans traditionally used blueberries as both food and medicine.
- They made a blueberry poultice to treat wounds and consumed them to support immunity during the winter months.
- Blueberries were often dried and mixed with cornmeal for long-lasting sustenance, like in pemmican.
2. Bilberries (Vaccinium myrtillus)
Medicinal Uses
- Eye Health: Known for improving vision, particularly night vision, due to their high anthocyanin content. They were historically given to pilots during World War II to enhance sight in low light.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Effective in treating conditions like arthritis and gastrointestinal inflammation.
- Blood Vessel Support: Strengthen capillaries and improve circulation, often used to manage varicose veins and hemorrhoids.
- Antimicrobial Effects: Historically used to combat infections, particularly urinary tract infections.
- Diabetes Management: Leaves and fruit have been used to lower blood sugar levels.
Historical Uses
- In European folk medicine, bilberries were used to treat diarrhea, scurvy (due to their vitamin C content), and urinary infections.
- Traditional remedies included bilberry tea for digestive issues and bilberry extracts for topical application on wounds.
- They were valued as a dye for fabrics and medicinal preparations due to their intense purple-blue color.
Key Differences in Medicinal and Historical Uses
- Geographic and Cultural Roots:
- Blueberries are native to North America and were widely used by Native Americans.
- Bilberries are native to Europe and Asia, with significant use in traditional European medicine.
- Eye Health:
- Bilberries are particularly renowned for improving vision and eye-related conditions, a use less emphasized in blueberries.
- Cognitive and Heart Health:
- Blueberries are more extensively studied for cognitive health and heart disease prevention.
- Gastrointestinal Benefits:
- Bilberries were historically used to treat diarrhea and stomach ailments, while blueberries are known for promoting general gut health.
- Anthocyanin Content:
- Both are rich in anthocyanins, but bilberries have a higher concentration, which may account for their stronger effects on vision and blood vessel health.
Conclusion
While both blueberries and bilberries share overlapping benefits as nutrient-rich, antioxidant-packed fruits, they each have unique historical and medicinal profiles. Blueberries are a staple in North American traditions, celebrated for their heart and brain benefits, while bilberries are integral to European herbal medicine, particularly for eye health and vascular support. Together, they represent two powerful allies in natural health and wellness.
| weight |
1oz ,4oz ,8oz ,16oz |
|---|
You May Also Like






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.